How Does Search Engine Optimization Work?
Article written by James Bledsoe, Director of the eCommerce Solutions Center
Search Engine Optimization Drives Online Sales
With the ever-growing increases in digital marketing spend for a business, there is one “customer acquisition improvement exercise” that can help improve your overall ecommerce ROI: search engine optimization.
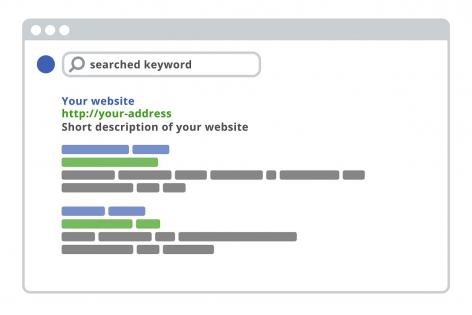
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of adding the content on your website in a way that appeals to the programming of a search engine’s search bots.
It is important that while doing SEO, you provide the necessary content on your product pages, so that a search bot can find your product information and provide it to the search engine results page, when you should be showing up in search.
Appealing to Search Bots
Search bots are robots that exist without physical form, and only as written programming instructions. The search bots only see your website content as written text, text written about objects (eg: video descriptions, picture alt text), and written text of a website URL (eg: backlinks, internal links).
Search bots are programmed by their search engines, and that programming determines what a webpage needs to have to meet its programmed requirements for showing up first in a search engine results page. Make sure you also take into consideration international SEO best practices to make sure that your focus and tactics aren’t for a domestic audience.
SEO is therefore can simply be described as checking your website and making sure that it meets the information needs programmed into search bots, which determines whether or not you show up for an international online sales opportunity.
How to Begin SEO for Your Website
You first need to understand if your website is functioning properly from a technical standpoint, and a great way to begin this process is with our SEO audit the WGR Gap Analysis Service, which is designed to provide you a report of how a search bot would rank your website in online search results.
After you have identified which areas of your website could use technical improvement through an SEO audit, you then should monitor your website analytics in order to track your ecommerce successes and progress as you implement recommended and needed SEO changes to your website.
Return to eCommerce Frontline Library Content
Looking for more ecommerce resources?