South Korea has earned a reputation as a leading global information and communication technology center. With its cutting-edge ICT infrastructure boasting the world’s fastest internet speeds and tech-savvy customers, the country is home to global leading electronics and IT companies such as Samsung Electronics, SK Hynix, LG Electronics and Naver. Korea is motivated to keep its reputation as a global ICT powerhouse by investing heavily into innovative technologies such as advanced semiconductor, next-generation network, Artificial Intelligence, big data, quantum computing, and cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity
ITA Code: ICT
NAICS Code: 541511
Overview
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 |
Total Market Size | 2,420.0 | 2,777.4 | 3,106.2 | 3,323.2 | 3,975.0 |
System & Product | N/A | 1,886.2 | 1,896.6 | 2,029.7 | 2,728.5 |
Consulting & Service | N/A | 891.2 | 1,209.6 | 1,293.5 | 1,246.4 |
Exchange Rate: 1 USD | 1,131 | 1,110 | 1,165 | 1,180 | 1,145 |
Source: Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea Information Security Industry Association (KISIA), 2022, Unit: $ millions.
As the world becomes more interconnected, cyberattacks have become more serious and sophisticated. Due to the focus of global hacker groups and cyber terrorists, cyberattacks are better organized, more persistent and executed on a larger scale. That focus broadened to include not just critical infrastructure but also private sector assets. The borderless nature of the internet is contributing to the vulnerabilities of certain devices and data storage.
With South Korea’s high degree of network connectedness, high penetration of mobile devices, and significant intellectual property, the country has become a prime target for cyberattacks. Cyberattacks in South Korea continue to increase in both frequency and complexity. South Korea was hit by a daily average of 1.2 million hacking attempts in 2022 according to a report published by the National Intelligence Service. The latest attacks on South Korea include the use of advanced malwares and ransomwares, supply chain attacks, crypto-jacking and zero-day attacks.
Not surprisingly, as the awareness of cyber vulnerabilities became apparent, the market demand for cybersecurity products and services in Korea continues to grow. According to a Korean government survey in 2022, for the past five years, the cybersecurity market grew at a CAGR of 13 percent reaching $4.0 billion in 2021. Also, the expansion of cloud computing, the multiplication of digital devices, and the increased digital activity that Covid-19 spurred is contributing to the growth of the cybersecurity market.
South Korea deems cybersecurity as a matter of national security. Although the country boasts one of the world’s fastest IT infrastructures, it also has an infrastructure that is vulnerable to cyberattacks. The frequency and gravity of recent cyberattacks prompted the South Korean government to re-evaluate its cybersecurity strategy. In 2019, led by the office of the President, the ROK government announced its first National Cybersecurity Strategy. This strategy includes strengthening partnerships with foreign countries and companies and expanding investment to the domestic cybersecurity industry. In 2022, to accelerate the promotion of its cybersecurity industry, the Korean government established the “Strategic Plan to Foster Data Protection Industry” and the “Digital Strategy of Korea”.
There is a growing number of domestic and U.S. companies providing cybersecurity services in Korea. There are 669 cybersecurity firms registered in Korea. While most of these firms have developed their own products, some are opened to partnering with small and medium sized exporters from the United States. These Korean companies are interested in filling gaps in technology and product/service line-up, in order to better help their clients meet a wide range of cybersecurity needs.
To enter the local public sector, foreign cybersecurity companies must understand local requirements. For example, local public agencies require companies to receive additional verification even if their products have already received Center for Cybersecurity Research and Analysis (CCRA) certification outside of the country. Also, depending on the product type and end-users, foreign companies should obtain security assurances such as the Korea Cryptographic Module Validation Program (KCMVP) and the Security Function Test Report before they can supply to public agencies in Korea.
Sub-Sector Best Prospects for 2023
The Korean public and private sectors predict that the key sub-sectors for the domestic cybersecurity market in 2023 include solutions for ransomware, cloud security, and supply chain risk management (see below chart).
NIS | KISA | Ahnlab | Samsung SDS |
Advanced Hacking Tools | Cyberattacks from International Hacker Groups | Multifaceted Extortion using Ransomware | Cloud Security |
Hacking for Social Disorder | Advanced Ransomware | Parasitic APT | Account Takeover |
Ransomware | Cloud Security | Zero-day Vulnerability on Core Assets | Advanced Ransomware |
Supply Chain Risk Management | Advanced Persistent Threat on Society | Supply Chain Security for Mobile Devices | Supply Chain Risk Management |
Cyber Espionage on Advanced Technology & Security Information | Supply Chain Cybersecurity | Security for Digital Assets | Hacking using AI |
Source: National Intelligence Service (NIS), Korea Internet and Security Agency (KISA), Ahnlab, Samsung SDS, 2022
Opportunities
Due to its leads in advanced ICT infrastructure and geopolitical factors, South Korea is an attractive market for U.S. firms seeking to test cybersecurity solutions before deployment in other markets in Asia. While firms that produce sophisticated products for critical infrastructure and edge devices are more likely to succeed, there are also opportunities for firms that provide cybersecurity related consulting and training services. Overall, the Korean market favors the quality and reliability of U.S. technologies and demand for American products is expected to continue.
To enter the cybersecurity market, CS Korea recommends that U.S. technology firms to partner with qualified and capable South Korean companies that maintain existing sales networks in both private/public sectors and are fully aware of local market characteristics and unique regulatory requirements. In the long term, it is recommended to consider employing a local hire or establishing a local office to provide prompt technical support and overcome possible communication issues with end customers.
Resources
Trade Shows
SECON & eGISEC (April / Seoul)
First hosted in 2001, SECON & eGISEC is Korea’s largest security exhibition covering all sectors of both cyber and physical security. In 2023, 355 companies from 10 countries attended the event and exhibited their products and solutions.
International Security Conference (October / Seoul)
Hosted by Ministry of Interior and Safety, ISEC is the largest cybersecurity conference in South Korea. The conference provides 35 sub-sessions and opportunities to engage with relevant domestic ministries and companies.
Key Contacts
· Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT)
· National Intelligence Service (NIS)
· Korea Internet and Security Agency (KISA)
· Korea Information Security Industry Association (KISIA)
Local Contact
U.S. Commercial Service Korea
U.S. Embassy Seoul
188 Sejong-daero, Jongro-gu
Seoul 03141, Korea
Tel: 82-2-397-4535
office.seoul@trade.gov
https://www.trade.gov/south-korea
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
ITA Code: ICT
NAICS Code: 541715
Overview
More companies in South Korea are using AI to accelerate their digital transformation efforts by increasing automation of tasks and reducing costs. According to a survey from the International Data Corporation (IDC) in 2022, the country’s spending on AI was expected to reach $824 million in 2021. IDC also forecasted that the spending would grow at a CAGR of 15 percent reaching $1.6 billion in 2025.
Major Korean ICT companies are aggressively pursuing AI technologies. Two leading electronics companies - Samsung and LG Electronics, the top internet companies - Kakao and Naver, and the major telecom companies - SK and KT, have invested significantly in AI. For example:
- Samsung Electronics opened seven AI centers in five countries and is working on various projects such as advanced machine learning algorithms, AI chips, and large language models.
- Naver, Korea’s largest search engine and portal site, acquired a Xerox AI research center Europe in 2017 and is developing its own core AI engines for large language modeling, speech/image recognition, and text analytics, etc.
- KT, the second largest mobile carrier in Korea, committed $1.2 billion in investment for its AI/robot business through 2027.
Also, startups are leading AI in South Korea. Many in the country see the creation and development of AI startups and businesses as vital to building a strong AI ecosystem. A number of ROK government agencies have created AI-oriented startup incubation programs to help develop emerging AI businesses. Also, the country’s thriving VC ecosystem is leading the AI startups expansion. Currently, South Korea is home to approximately 400 AI startups.
Regardless of the size of the firms or the solution’s countries of origin, Korean companies are seeking cutting-edge technology and applications to enhance their AI capabilities and implement AI technologies to their products and services. Also, more of these companies are looking for technology/business partnerships with foreign AI companies and startups.
The ROK government has expressed its ambition to position itself as a global contender in AI technologies markets. ROK officials see AI as a crucial element for the country’s prowess in the ICT sector and are committed to making Korea an AI powerhouse. In support of this goal, in 2019, the ROK Government announced its first national AI strategy which included focusing on heavy investments in AI infrastructures and greater use of AI technologies across all industries. In 2022, the government released the Digital Strategy of Korea, the national strategy for digital transformation, which envisioned state-led industrial and educational efforts on the potential opportunities in AI. According to the strategy, the country will invest $1 billion in researching core AI and AI semiconductor technologies.
The ROK recognized that there is an engineering gap for experienced and skilled AI talent and thereby designated fifteen local universities as AI engineering schools and four national universities as AI research centers as of 2023. The movement is also to realign the national R&D capabilities to specialized in various AI research fields such as AI ethics, data, and AI convergence with other industries.
Sub-Sector Best Prospects
· AI Chip: By reducing the need to send and receive data over the internet, AI chips enable devices to perform intensive AI computations on all IT devices. All the major Korean ICT companies are investing heavily on developing AI chips for adding new products and services based on AI.
· Large Language Model/Generative AI: More Korean companies are interested in leveraging LLM in various applications such as search engines, contents, healthcare, and finance.
· Explainable AI: As the influence of AI technology spreads across sectors such as healthcare, finance and defense, companies are looking for the AI models that provide greater interpretability for users and guarantee the reliability of the model.
Resources
Trade Shows
AI EXPO Korea (April, Seoul)
Organized by the Korea AI Association, AI Expo is the largest annual AI exhibition in South Korea. In 2021, 138 Korean/global companies and 23,263 participants attended the event. The exhibition also featured technology seminars and network events.
AI Korea/AI World Congress (September, Busan)
AI Korea, hosted by Busan Metropolitan City, focuses on Korea’s AI capabilities and provides a platform for global companies to convene and discuss trends in AI. This year’s theme will include AI application for smart cities, mobility, healthcare, manufacturing, and government policy in AI.
Other Resource
· Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT)
· National Information Society Agency (NIA)
· Korea Artificial Intelligence Association (KORAIA)
· Artificial Intelligence Industry Association (AIIA)
Local Contact
U.S. Commercial Service Korea
U.S. Embassy Seoul
188 Sejong-daero, Jongro-gu
Seoul 03141, Korea
Tel: 82-2-397-4535
office.seoul@trade.gov
https://www.trade.gov/south-korea
Cloud Computing
ITA Code: ICT
NAICS Code: 548210, 541512
Overview
With Korean enterprises and government institutions adopting cloud services with increasing frequency, the cloud computing market in Korea is expected to grow at a faster rate than other IT services market sectors. According to Gartner, the South Korea cloud computing market reached $4.0B in 2022, a 23 percent increase over the previous year.
Global cloud service providers such as Amazon Web Services, Microsoft, and Google have led the cloud computing market in Korea. To further increase their market share, the global players have accelerated their investments in Korea. Global cloud service providers have opened multiple data centers in the peninsula. The recent boost in demand for cloud computing has caught the attention of Korean companies. Major Korean IT companies (Naver, NHN) and mobile carriers (KT) have entered the market. Also, as more information infrastructure and company data have been migrated into the cloud, more Korean companies are starting to use software/services on the cloud.
In the public sector, South Korea was one of the first countries to establish a national cloud computing strategy. The government presented its first blueprint for the promotion of the cloud computing industry in 2015. To stimulate the sector, the government released new guidelines in 2018 on the use of the private cloud services for the public sector. The guidelines designate cloud computing as an alternative measure to network separation for cybersecurity and for storage of important data such as financial information. In 2022, the government included cloud computing as one of the sub-areas for its national digital strategy with the goal of promoting high-speed/energy efficient cloud infrastructures and transitioning the country’s software market to the Software as a Service model.
To enter the Korean public cloud market, foreign cloud companies face significantly more restrictions and must understand certain market specific requirements regarding personal information and data protection. One of the key regulations is the cloud security certification for public sector cloud service procurement. Although their presence is expected to strengthen further within the private sector, the global CSPs are facing challenges in the public sector. The Korean government introduced the Cloud Security Assurance Program (CSAP) which requires foreign CSPs to create a separate Korea-unique product for all central/local government agencies, affiliated public institutions, educational institutions, and public hospitals. The government recently amended the program which eases certain requirements on physical system location, backup system, and operation management; however, industry assesses that the new certification process still remains complex and ambiguous on some requirements such as the common criteria requirements and data protection measures.
Opportunities
Thanks to the continuing cloud migration of the private sector, the Korean cloud market is forecasted to grow to $5.2B in 2023 according to Gartner. The U.S. cloud service companies will continue to be the leading providers of this Infrastructure as a Service sector. As more local private companies seek to adopt various and customized applications and services on their cloud, there will be increasing opportunities in the SaaS sector. U.S. SaaS companies will be able to extend their business to the Korean market by using local cloud service providers. Also, cloud management service is another promising sector as a smooth cloud migration is critical for local companies new to cloud computing.
Resources
Trade Shows
· Grand Cloud Conference (December, Seoul)
· Cloud Expo Korea (September, Busan)
Key Contacts
- Ministry of Science and ICT
- Korea Association of Cloud Industry
- Korea Internet & Security Agency
Local Contact
U.S. Commercial Service Korea
U.S. Embassy Seoul
188 Sejong-daero, Jongro-gu
Seoul 03141, Korea
Tel: 82-2-397-4535
office.seoul@trade.gov
https://www.trade.gov/south-korea
Semiconductor
ITA Code: ICT
NAICS Code: 334413
Overview
The semiconductor industry is one of South Korea’s core industries. The industry accounts for 8 percent of the national GDP. Semiconductors (chips) are the largest export item ($129 billion) which made up 18.9 percent of the country’s total exports in 2022 according to the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Thanks to solid demand for chips for new IT devices, and innovative services like artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing, the global demand for chips has grown, resulting in the industry posting strong growth over the past few years.
South Korea is a global leader in the memory chip fabrication. As of 2022, two South Korea memory giants – Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix held 73 percent of the global DRAM market share and 51 percent of the NAND flash market according to TrendForce. Also, Korea has many small and medium-sized companies producing various semiconductor products and equipment. There are 4,464 semiconductor related companies including fabless, foundry, packaging, materials and equipment makers in South Korea according to a survey from the South Korean government.
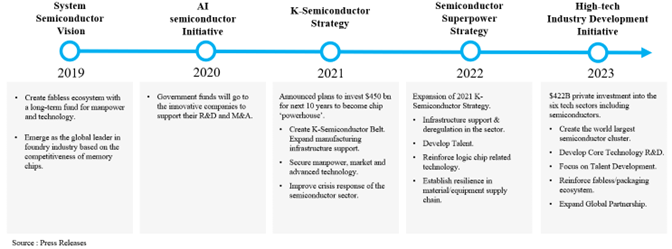
While South Korea is considered a leader in technological competitiveness in memory chips, other types of semiconductor products such as microprocessors and sensors are less competitive globally. In order to expand the country’s semiconductor leadership beyond memory chips, the country announced a series of national development plans to support the industry.
The most recent government plan announced was the high-tech industry development initiative (2023). The plan calls for 550 trillion won, equivalent to $422 billion, of national investment in the six leading tech sectors including semiconductors. The other five sectors are flat screen displays, batteries, biopharmaceuticals, future vehicles, and robots. The initiative laid out the Republic of Korea (ROK)’s ambitious goal to build the world’s biggest semiconductor manufacturing cluster over next two decades. Also, the initiative includes a national R&D goal including core semiconductor technologies, semiconductor talent development, strengthening of the country’s non-memory sector ecosystem, and expansion of global partnerships.
Also, in March 2023, South Korea revised the Restriction of Special Taxation Act called K-Chips Act, which will increase tax credits from the current 8 percent to 15 percent for semiconductor facility investment by large companies and from 16 percent to 25 percent for that by small and medium-sized companies.
Opportunities
The rapidly growing AI and cloud computing markets are key growth factors for semiconductors. Market demand will be driven further by increasing connectivity through innovative technologies such as next-gen network, connected cars, and IoT. As one of the world’s major semiconductor manufacturers, Korea will be among the primary beneficiaries of such technology innovations. Moreover, as the total production increases, more equipment and materials will be needed, including imports.
There is an enormous market for suppliers of equipment, materials, and services for semiconductor fabrication in South Korea. For example, in 2022 South Korean companies purchased $22 billion of semiconductor equipment representing 20 percent of the global semiconductor equipment market according to a survey by SEMI. Most of the equipment was provided by foreign semiconductor equipment makers mainly from the United States, Japan, and Netherlands. Also, South Korea imports significant amount of semiconductor materials from the United States and Japan.
To retain its leadership in the semiconductor market, local companies are proactively investing in expanding their advanced fabrication capabilities.
· Samsung Electronics: U.S. Expansion: In 2022, Samsung broke ground on its second foundry chip production line in Taylor, Texas, investing $17 billion in buildings, property improvements, machinery and equipment. The facility is expected to be operational in 2024. South Korean Expansion: In 2023, the company also announced that it will invest $230 billion to build five advanced fabrication plants in South Korea by 2042.
· SK Hynix: In 2019, SK announced a $100 billion long-term global investment plan which includes building four fabrication plants by 2029. In 2020, the company signed a $9 billion deal to acquire Intel’s NAND flash memory fabrication facilities and business. In 2022, the company announced it will build its first chip packaging facility in the U.S.; the location is still undetermined.
The ROK is also highly interested in investing in the next step of miniaturizing semiconductors with innovative processes such as utilizing extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography, developing new materials, and diversifying its supply chain beyond existing suppliers.
Resources
Trade Shows
SEDEX (October, Seoul)
Organized by Korea Semiconductor Industry Association (KSIA), the exhibition covers the full spectrum of the semiconductor industry supply chain and products including logic, memory, sensor, equipment, and material. During the 2022 event, 253 companies including Samsung Electronics and SK hynix presented their products to more than 60,000 participants.
SEMICON KOREA (February, Seoul)
Focusing on semiconductor equipment and materials, SEMICON is one of the major trade events for semiconductor industry in Korea. In 2022, more than 450 global companies exhibited at the event.
Key Contacts
· Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy
· Ministry of Science and ICT
· Korea Semiconductor Industry Association
Local Contact
U.S. Commercial Service Korea U.S. Embassy Seoul188 Sejong-daero, Jongro-gu
Seoul 03141, Korea
Tel: 82-2-397-4535
office.seoul@trade.gov
https://www.trade.gov/south-korea