Overview
The IT industry in Romania is experiencing constant development, and new trends are emerging year after year, making it one of the most significantly growing markets in the country. 2023 is a critical year for the technology sector in Romania, as the government has set forth several initiatives to help digitalize small and medium-sized enterprises. For example, the PNRR Digitalization of SMEs program is vital to this effort and could significantly impact the country’s tech sector. The program could open new opportunities for tech companies to provide services and products to these businesses.
Romania’s digital economy could be worth €52 billion by 2030, accounting for almost ten percent of the country’s GDP. ICT grew around eight percent annually in Romania from 2017 to 2021— though not strongly enough to close the ICT gap with other “Digital Challenger” countries. The country, however, is showing signs of a developing better ICT infrastructure, which may lead to higher digital literacy among the population. Its ICT fundamentals may catch up with average Digital Challenger levels and could be the main growth driver of Romania’s digital economy in the coming years. Spending on digital equipment and e-commerce will grow as digital fluency and digital use increase.
Romania scores high in terms of telecom networks and Internet speeds. Although the measures taken during the COVID-19 crisis significantly increased demand for Internet capacity, telecom operators succeeded in maintaining and quite often improving the quality of the electronic communication services due to significant infrastructure investments. Thus, companies in Romania have transitioned to remote working capabilities without significant disruptions.
Thus, it comes as no surprise that Romania ranks 6th place in the top of the fastest-growing countries for fixed broadband and 43rd place among the fastest countries for mobile internet. With the introduction of 5G services in Romania, the identical scores 2nd place in downloading speed and 1st place in upload speed, proving the high quality of the Romanian mobile networks.
Romania’s ICT sector is comprised of manufacturers of electronic components, computers and peripheral equipment, communication equipment, consumer electronics, and magnetic and optical recording media; software publishing; telecommunications; information technology services; web portal, data processing, web page administration, and related activities; repair of computers and communication equipment.
The country’s center point for IT development is the capital region of Bucharest (63% of nationwide revenue), followed by business centers in the North-West (18%); West (5%); Central (6%); and North-East 5(%).
Romania is the leader in Europe and sixth in the world regarding the number of certified IT specialists per 1,000 inhabitants, larger than in the US or Russia.
The Digital Agenda for Romania also sets priorities for crucial sectors for the Romanian economy and society: Employment, Research, and Development (R&D), Climate Change and Energy Sustainability, Education, and Fighting Poverty and Social Exclusion.
Software and IT Services in Romania
The Romanian IT service software market is growing substantially and appears likely to become the most critical contributor to GDP in the medium to long run.
Research and Development
Romania has an essential tradition in research, development, and innovation in the technical field. Engineers’ technical expertise and lower labor costs have helped attract exciting and more significant projects into the local industry. Industry clusters can be found in major university cities: Bucharest, Cluj-Napoca, Iasi, Timisoara, Craiova, and Brasov.
Market Demand
Software Development
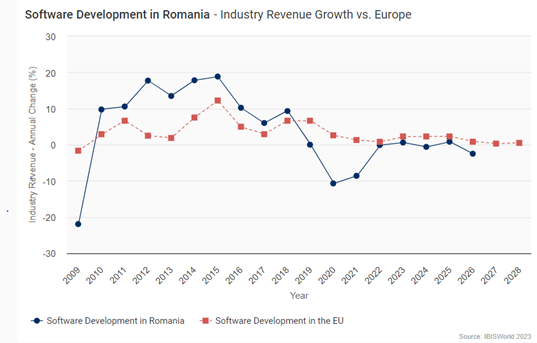
The market size, measured by revenue, of the Software Development in Romania industry is €3.2bn in 2022.
There are nearly 192,000 developers in Romania as of 2023. The number of people pursuing a tech career is growing, since just a few years prior, in 2020, there were roughly 140,000 software engineers in the country.
The market size, measured by revenue, of the Software Development in Romania is €3.2bn in 2023. The market size of the Software Development in Romania industry has declined 5.4% per year on average between 2018 and 2023.
There are 50,829 people employed in the Software Development in Romania industry as of 2023.
The average Software Development in Romania business in Romania has 6.3 employees.
There are 8,022 Software Developments in Romania businesses as of 2023, a decline of -1.4% from 2022.
Market Entry
Selling through an established local Romanian channel partner is most U.S. manufacturers’ lowest-risk market entry strategy. However, when selling to Romanian government departments, it may be necessary to establish a direct business presence in Romania, especially when competing for projects related to national security. Cooperation with ANSSI (www.anssi.ro), the essential local association in cybersecurity, offers U.S. companies interested in the Romanian market the best approach to finding partners, information about the market, and business opportunities with the public sector.
Companies can benefit from an additional deduction of 50% from the eligible expenses for research and development. Moreover, accelerated depreciation may be applied for devices and equipment used in research and development activity. For significant investments, state aid schemes or individual aid may be available.
Romania has laws on electronic commerce, online copyrights, electronic signature, electronic payment, online advertising, personal data protection, cybercrime, internet pornography, and electronic communications.
The government also developed draft laws for minimum security conditions of digital systems for the Public Administration and national electronic records.
Leading Sub-Sectors
There are significant opportunities for expertise, products, and services in the following categories:
- Incident response and disaster recovery
- Software reporting, forensic tools, and security information
- Interoperable software products and technologies
- Emergency response and shared intelligence
- Cybersecurity
- Educational software
Opportunities
One of the top priorities of the Romanian government’s IT strategy is the digitalization of the Public Sector, with the implementation of associated cybersecurity programs.
Romania’s ICT sector opportunities are enhanced by the European Recovery and Resilience Facility and subsequently by Romania’s National Recovery and Resilience Plan, which is based on the green and digital transition.
ICT is present in all the six pillars that make up the recovery plan, with two of them strongly related to the digital transformation of Romanian society.
The second Pillar (Digital Transformation) is based on four priorities:
- Public services digitalization
- Digital skills
- Secure and resilient digital infrastructures
- Digital transformation of SMEs
The main component of this pillar is the Governmental Cloud and digital public systems, with a budget of $2.08 billion. It consists of four reforms and 19 investments, including Governmental Cloud, electronic identity cards for 8.5 million people, and skilling/up-skilling/re-skilling for 30,000 civil servants and 100,000 citizens at 65 organizations that will improve their cyber security knowledge.
On the other hand, the third Pillar (Smart, Sustainable, and Inclusive Growth) includes another important Component (Support for business, research, development, and innovation) and proposes two reforms and five investments with a total budget of $2.6 billion. Among the results assumed by those investments related to IT&C are that at least 3,000 SMEs must undergo a digital transformation process. Also, funds for digitalization, climate action, and other areas of interest are co-managed with the European Investment Bank as an implementing partner and support for at least three organizations with expertise in microelectronics to join projects of the European Partnership for Key Digital Technologies.
One of the top priorities of the Romanian government’s IT strategy is the digitalization of the Public Sector, with the implementation of associated cybersecurity programs.
The Ministry of Research, Innovation, and Digitization on the government cloud has initiated an emergency ordinance. A milestone in PNRR (National Recovery and Resilience Plan) was an investment of almost €600 million and, more importantly, a crucial first step in Romania’s digital transformation. Also referred to as Sovereign Cloud, this transformation will allow public institutions to communicate with each other, leading to productivity, development, and modernization.
Some objectives are:
- Public-private partnerships will be provided through the hybrid cloud. This hybrid system will allow for an optimal mix between state-of-the-art private and public methods that guarantee the protection of citizens’ data.
- virtual marketplace app store for public institutions
- access logging and citizen notifications when personal data is accessed through a blockchain solution.
Events
• Smart City Expo World Congress, November 7-9, 2023 ● Barcelona, Spain
• Web Summit, November 13-16, 2023 ● Lisbon, Portugal
• Consumer Electronics Show, January 5-8, 2024 ● Las Vegas, NV
• RSA Conference (Cybersecurity), May 6-9, 2024 ● Chicago
• Trade Winds Romania, May 9-10, 2024 ● Bucharest, Romania
• Trade Winds Europe & Eurasia Forum and Trade Mission, May 13-15, 2024 ● Istanbul
Contact information:
Alina Capat, Commercial Assistant