Overview
Table 1: Japan’s Semiconductor Market Size, Units: Billions USD
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
Market Size (Japan) | 48.158 | 48.751 | 47.410 | 51.886 |
Y-on-Y Growth (Yen basis) | 10.2% | -2.9% | 1.4% | 9.4% |
Exchange Rate | 131.4 | 140.4 | 150.5 | 148.9 |
Source: Data from WSTS statistics.
Japan Market Overview and Positioning
Buoyed by sales of AI semiconductor chips, the global semiconductor market is projected to reach $1 trillion by 2030. Japan’s market is also steadily expanding and is estimated to reach over $51 billion by 2025. A key driver of the Japanese semiconductor sector’s steady growth has been increased investment in logic integrated circuits (ICs) and memory ICs. The Government of Japan continues to prioritize and fund the country’s semiconductor and AI sectors. According to an April 2024 Nikkei Asia report, Japan proportionately spends more to support its semiconductor industrial sector than the United States and other Western countries. Japan has provided 0.71% of its GDP, or $25.7 billion, to fund its semiconductor industry over a three-year period.
In the 1980s, Japanese companies accounted for more than 50% of the global semiconductor market. However, Japan lost its dominant semiconductor market position, with U.S. companies emerging as global semiconductor design leaders and Taiwan’s semiconductor industry establishing itself as the world’s semiconductor manufacturing leader. Japan hopes to reclaim some of its previous semiconductor predominance by focusing resources on mass producing advanced 2-nanometer (nm) semiconductor chips – an industrial feat that has not yet been accomplished but which Taiwan’s semiconductor manufacturer TSMC hopes to achieve in the latter part of 2025. Rapidus, a government-funded start-up, plans to begin mass producing 2-nm chips in 2027. Rapidus announced on July 18 that it had successfully verified the operation of a 2-nanometer-class prototype transistor at its first fabrication facility in Chitose, Hokkaido. Currently, the most advanced semiconductor chip manufactured in Japan is a 40-nm chip. For Japan to leap-frog from manufacturing 40-nm to 2-nm semiconductor chips, the Government of Japan founded and funded Japan’s Rapidus Corporation in 2022, albeit with a token contribution from eight Japanese companies. To date, the Government of Japan has provided over $6.1 billion in funding to Hokkaido-based Rapidus. The company has collaborated with international partners such as IBM on its 2-nm chip development efforts. More than 100 Rapidus engineers have traveled to IBM’s New York-based R&D center to jointly develop technology for manufacturing 2-nm chips at Rapidus’s facility in Hokkaido.
While Japan ostensibly focuses funding and resources to grow its semiconductor chip manufacturing capacity, the country continues to dominate certain semiconductor equipment and materials segments. As reported by the Brookings Institute in June 2024, Japan has almost 88% global market share for semiconductor coater/developers, 53% global market share for silicon wafers, and 50% global market share for photoresists.
Leading Sub-sectors
Semiconductor Equipment
Table 2: Japan’s Semiconductor Equipment Market Size, Units: Billions USD
| 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | 2025 |
Market Size | 29.849 | 22.810 | 29.472 | 31.284 |
Y-on-Y Growth (Yen basis) | 11.0% | -9.2% | 20.7% | 4.9% |
Exchange Rate | 131.4 | 140.4 | 150.5 | 148.9 |
Source: Data from WSTS statistics.
One of the leading Japan semiconductor sub-sectors is semiconductor equipment. According to the Semiconductor Equipment Association of Japan (SEAJ), Japan’s semiconductor equipment market size in 2023 shrank by 19% to $22.8 billion because companies reduced their investments in logic foundries and memory facilities. However, SEAJ analyses indicate that Japanese semiconductor equipment companies experienced stable sales in 2024 based on new investments in data centers as well as new developments in central processing units (CPUs) and generative AI. SEAJ projected that Japan’s semiconductor equipment sales increased by 27% in 2024 and will further increase by 10% in 2025.
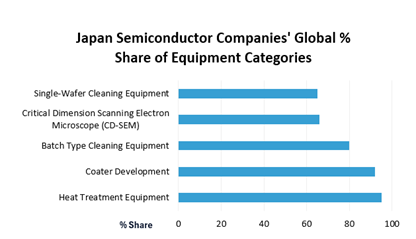
As indicated in the graph below, Japanese semiconductor equipment companies account for between 60-80% of the global market for single-wafer cleaning equipment, critical dimension scanning electron microscopes, and batch type cleaning equipment. For coater development and heat treatment equipment, Japanese semiconductor equipment companies represent around 90% or more of the global market share.
Semiconductor Materials
Japan’s semiconductor material manufacturers play critical roles in the supply chain with high-purity, high-performance materials essential for semiconductor manufacturing. Many of these companies are recognized for their essential materials in existing and next-generation semiconductor manufacturing and have advanced technological capabilities.
Shin-Etsu Chemical and SUMCO dominate the global silicon wafer market segment with approximately 90% of the market. In the photoresist field, several Japanese firms such as JSR and Tokyo Ohka Kogyo hold about 90% of the global market. Japanese companies account for approximately 30% of the global photomask market.
In addition, although Japan’s Ajinomoto is generally known as a manufacturer of food flavor enhancer MSG or monosodium glutamite, the company also manufactures Ajinomoto Build-Up Film resin that provides electrical insulation in the semiconductor chip packaging process.
Opportunities
The Government of Japan’s priority initiative to mass produce 2-nm semiconductor chips and enhance the country’s semiconductor ecosystem creates an opportunity for U.S. semiconductor companies seeking growth opportunities in Japan. With the establishment of Rapidus and a new chip manufacturing hub in Hokkaido, U.S. companies engaged in semiconductor equipment and material manufacturing activities may contemplate export and service opportunities with Rapidus and its R&D partner IBM in furtherance of Rapidus’s 2-nm manufacturing efforts.
In addition to Rapidus and IBM efforts in Hokkaido, other Japanese companies engaged in semiconductor manufacturing efforts provide opportunities for U.S. semiconductor companies to explore. Japan’s Kumamoto Prefecture has experienced accelerated growth over the past three years following TSMC’s announcement that it would build two semiconductor manufacturing facilities in the prefecture. In addition, Japan’s Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. announced that it will build a new plant in Gunma Prefecture to expand its semiconductor lithography materials business.
In the United States, Japan semiconductor material company Resonac announced “US-JOINT,” a new consortium of ten U.S. and Japanese semiconductor and equipment companies that will engage in semiconductor back-end R&D, specifically efforts to verify the latest requirements for advanced device semiconductor packaging. This Japan-led semiconductor initiative in Silicon Valley represents another opportunity that U.S. semiconductor companies may explore for purposes of learning more about Japan-U.S. semiconductor industry efforts.
As for exhibitions, SEMICON Japan, one of the largest global semiconductor trade shows and exhibitions, presents a highly advantageous platform for U.S. semiconductor-related enterprises to enhance their brand presence in Japan. SEMICON Japan 2025 will be held December 17-19, 2025, and offers opportunities for U.S. semiconductor companies to engage with potential Japanese customers and business partners.
Resources
Government of Japan Agencies
Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry
Semiconductor Organizations
SEMI (Semiconductor Business Association)
Semiconductor Equipment Organizations
Events
SEMICON Japan
December 17-19, 2025
For additional information about Japan’s semiconductor business sector, please email Commercial Service Japan (“CS Japan”) at office.tokyo@trade.gov or Ms. Atsuko Shimada at Atsuko.Shimada@trade.gov.